SRM Supported Frameworks
The Envizi Sustainability Reporting Manager tool covers many ESG Frameworks. While Envizi seeks to cover the most popular frameworks with the broadest coverage, there may be some frameworks that are not covered. In some cases Envizi has created other tools and reports to meet the framework requirements, as we currently do for GRESB and CDP.
All available frameworks can be enabled by request, but Envizi seeks to provide a streamlined experience so only those frameworks that are needed by the organization are enabled.
For an overview of ESG Framework landscape more generally, see here.
Attribution
Title: BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITY & SUSTAINABILITY REPORTING FORMAT
Source: https://www.sebi.gov.in/sebi_data/commondocs/may-2021/Business responsibility and sustainability reporting by listed entitiesAnnexure1_p.PDF and https://www.sebi.gov.in/sebi_data/commondocs/jul-2023/Annexure_II-Updated-BRSR_p.PDF
Licence: https://www.sebi.gov.in/website-policy.html
For more information on the BRSR standards, see the source links above.
Attribution
Title: ANNEX to the Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) .../... supplementing Directive 2013/34/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards sustainability reporting standards
Licence: This content is provided under a ‘Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence’.
For more information on the ESRS standards, see Annex 1 found on the European Commission website using the source link above.
GRI Disclaimer
The GRI Standards are used by IBM Envizi under licensed authority from GRI. GRI, as Licensor of the copyright in the GRI Standards, verified and validated the authentic and accurate representation of the GRI Standards by Licensor in (Licensee's Authorized Product). This verification was limited to ensuring the maintenance of the integrity, authenticity and accuracy of the Licensed Content. GRI therefore makes no implied or actual representations or warranties as to the correctness, compliance, trustworthiness, fitness of purpose or quality of IBM Envizi or any products resulting therefrom; or of Licensee’s use of the GRI copyrighted content; and expressly disclaims any implied or express representations that any report produced by Licensee meets the standards of an approved GRI Standards Report.
The GRI Framework is structured into the following categories:
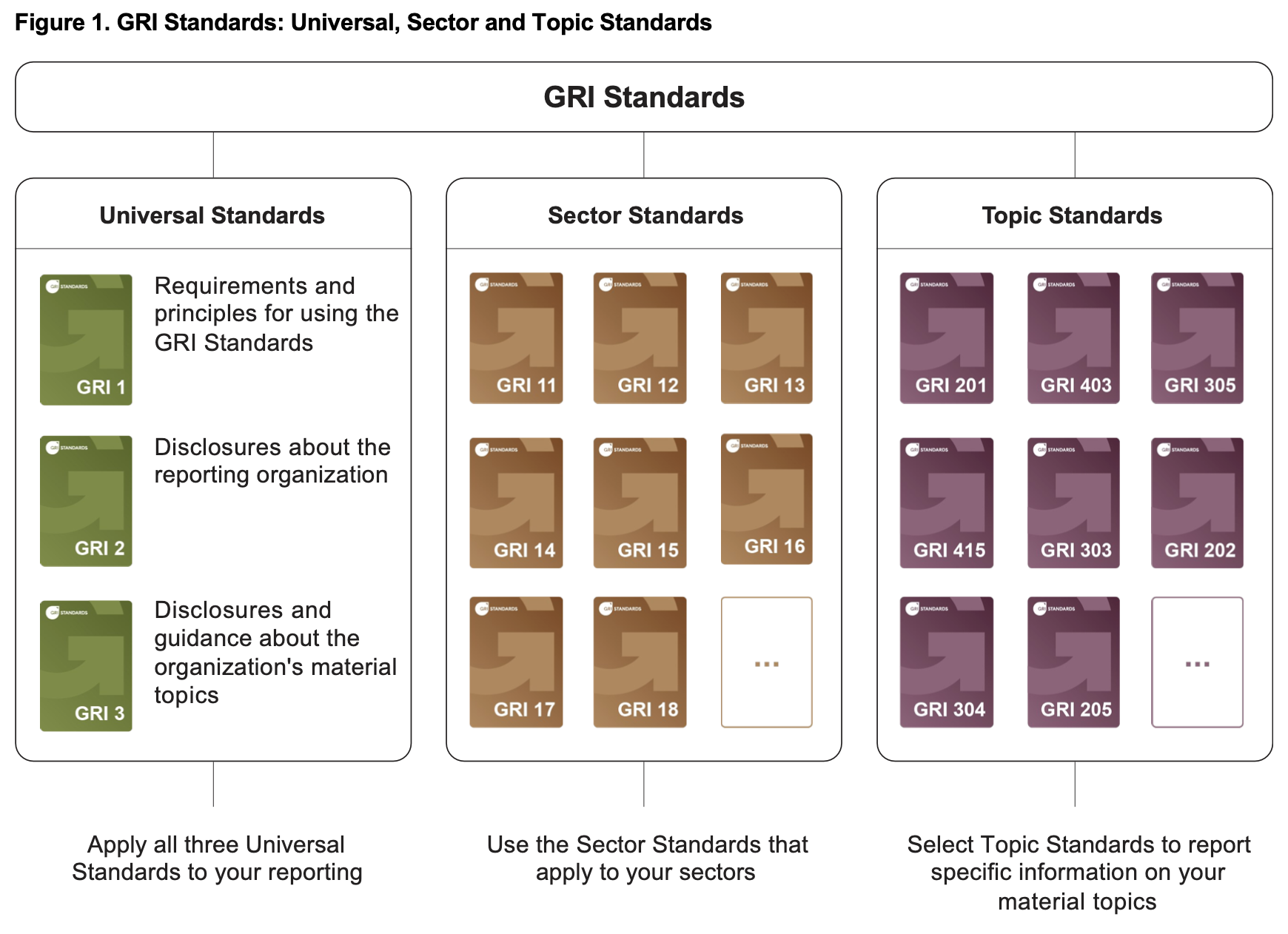
This figure was sourced from GRI 2, page 6.
Envizi provides support for all Topic Standards and will be adding support for all Sector Standards as they are released. Currently GRI 11, 12 and 13 are supported. See here for more information.
The Aoetearoa New Zealand Climate Standards (NZ CS) are sustainability reporting standards published by the New Zealand government. The primary objective of the New Zealand Climate Standards is to facilitate investment in endeavors that align with New Zealand’s transition toward reduced greenhouse gas emissions and increased resilience to climate change effects. The Climate Standards apply to entities required to prepare climate statements or group climate statements pursuant to the Financial Markets Conduct Act 2013 section 7(a).
This regulation is based on the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework and are strongly aligned with other international standards. In this sense, the Climate Standards require disclosure of what an entity is doing, but do not require an entity to take any action.
The Climate Standards are divided in three parts, NZ CS1, NZ CS2 and NZ CS3. The three standards are designed as a package and it is important that they are read together.
NZ CS1 provides a structured approach for organizations to evaluate and address climate-related risks and seize opportunities associated with sustainability goals.
NZ CS2 outline a limited number of adoption provisions
NZ CS3 establishes principles and general requirements to enable the provision of high-quality climate-related disclosures.
Additionally, the External Reporting Board has published Staff Guidance to help entities prepare their required climate-related disclosures.
Disclaimer
The Aotearoa New Zealand Climate Standards are published by the New Zealand government and can be consulted in the External Reporting Board Website
Ipieca is a global not-for-profit oil and gas industry association for environmental and social issues, headquartered in London. The association was established in 1974 as the International Petroleum Industry Environmental Conservation Association and changed its name in 2002. Member companies of Ipieca, the global oil and gas industry association for advancing environmental and social issues, the American Petroleum Institute (API), and the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP) have been collaborating on this important Guidance since 2005.
Company members contribute to Ipieca's budget according to an individually agreed percentage based on the volume of crude oil produced and petroleum products sold by each company and the number of geographical areas where the company has interests.
Ipieca is the industry channel into UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the UNFCCC, both concerned with climate change.
For more information on Ipieca, see here.
Attribution
The 'Sustainability reporting guidance for the oil and gas industry' framework is reproduced in the Sustainability Reporting Manager tool with permission from ipieca.
SASB Standards help companies disclose relevant sustainability information to their investors. Available for 77 industries, the SASB Standards identify the sustainability-related risks and opportunities most likely to affect an entity’s cash flows, access to finance and cost of capital over the short, medium or long term and the disclosure topics and metrics that are most likely to be useful to investors.
As of August 2022, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) of the IFRS Foundation assumed responsibility for the SASB Standards. The ISSB has committed to maintain, enhance and evolve the SASB Standards and encourages preparers and investors to continue to use the SASB Standards.
SASB Attribution
Envizi licenses and uses the SASB Materiality Map® Disclosure Topics, Accounting Metrics, and Technical Protocols in our work.
The SASB standards are organized into 11 sectors, which are sub categorized into 77 industries. To identify the industry (or industries) your organization may wish to report against, visit the SASB website and use the Materiality Finder.
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provides a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future. At its heart are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which are an urgent call for action by all countries - developed and developing - in a global partnership. They recognize that ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working to preserve our oceans and forests.
Attribution
Title: Sustainable Development Goals
Source: https://sdgs.un.org/goals
Licence: Permission to use text content granted by Rights and Permissions, United Nations Publications - [email protected].
Disclaimer: The use of the SDGs does not imply the endorsement of the United Nations of an entity, its products or services, or of its planned activities.
TCFD’s Goal: Given its remit from the Financial Stability Board, the TCFD is committed to market transparency. In our view, the success of the TCFD recommendations depends on widespread adoption by companies in the financial and non-financial sectors.
Through widespread adoption, financial risks and opportunities related to climate change will become a natural part of companies’ risk management and strategic planning processes. As this occurs, companies’ and investors’ understanding of the potential financial implications associated with transitioning to a lower-carbon economy and climate-related physical risks will grow; information will become more decision-useful; and risks and opportunities will be more accurately priced, allowing for the more efficient allocation of capital.
For more information on TCFD, see here.
Attribution
Content is provided according to the TCFD terms and conditions.
Source: TCFD Recommended Disclosures
No changes were made to source content.
The recommendations of the TNFD have been designed to meet the corporate reporting requirements of organisations across jurisdictions, to be consistent with the global baseline for corporate sustainability reporting and to be aligned with the global policy goals in the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. The TNFD disclosure framework consists of conceptual foundations for nature-related disclosures, a set of general requirements, a set of recommended disclosures structured around the four recommendation pillars of governance, strategy, risk and impact management, and metrics and targets. This is consistent with the approach of the TCFD and the ISSB’s IFRS Standards.
Attribution
TNFD content is used under a CC BY 4.0 licence.
Source: TNFD Recommended Disclosures
No changes were made to source content.
Corporate sustainability starts with a company’s value system and a principles-based approach to doing business. This means operating in ways that, at a minimum, meet fundamental responsibilities in the areas of human rights, labour, environment and anti-corruption. Responsible businesses enact the same values and principles wherever they have a presence, and know that good practices in one area do not offset harm in another. By incorporating the Ten Principles of the UN Global Compact into strategies, policies and procedures, and establishing a culture of integrity, companies are not only upholding their basic responsibilities to people and planet, but also setting the stage for long-term success.
UN Disclaimer
The United Nations Global Compact does not sponsor, endorse, review or otherwise express any opinion regarding IBM's products and/or services.
Attribution
UN Ten Principles of the UN Global Compact is public/unrestricted data.
The UNGC enhanced Communication on Progress has been designed to measure and demonstrate progress to stakeholders and the public on the Ten Principles and Sustainable Development Goals in a consistent and harmonized way, The CoP questionnaire concentrates on five main subject areas (governance, human rights, labor, environmental protection, and anti-corruption) aiming to assist collaborating organizations in tracking execution over the Ten Principles. The enhanced Communiqué on Progress demands the submission of a declaration by the CEO stating unwavering backing for the United Nations Global compact along with completing a digital survey concerning corporate actions linked to the Ten Principles and the SDGs. Both elements must be finished and submitted through the CoP digital platform between 01 April and 31 July annually.
The United Nations Global Compact does not sponsor, endorse, review or otherwise express any opinion regarding IBM's products and/or services.
Attribution
IBM Envizi ESG Suite cannot submit a UN Global Compact Communication on Progress on behalf of its users. UN Global Compact business participants are solely and individually accountable to fulfill their reporting requirements and for the content provided therein. For instructions on how to submit a CoP, please consult the UN Global Compact website.
Source:
No changes were made to source content.
