Factor Published Date Logic
Many environmental organizations (US EPA, IEA, DEFRA, NZ Department of Environment and others) will publish factors many years after the factors are effective. For example, in 2014 the US EPA published eGrid factors for electricity using data from 2010. This can cause problems for emissions reporting since some organizations want to report based on the latest available emission factors (published dates), while others want to use emission factors that align with the time period of their activity data (effective dates).
To avoid the issue of having to store and manage duplicate emission factors with different dates, or recalculating an organization's emissions when new factors are published, Envizi stores 2 sets of dates for a single factor: effective dates and published dates. The organization can then decide the point in time at which their data will switch from using the effective dates of an emission factor to the published dates. This page will explain how effective dates and published dates are used in emissions calculations and how to control which dates are used.
Calculation methodology
When an organization joins Envizi, they will typically request a historical data load. Once data is loaded, factors will be applied to their historical data. These factors are used to calculate emissions and energy and other unit conversions like mass, volume, etc. The standard calculation methodology used to source a factor uses a hierarchy of factor attributes that include factor sets, data types, sub types, effective dates and published dates.
The following table shows a timeline of data and visually represents how factors are applied to monthly activity data based on an organization's historical load date.

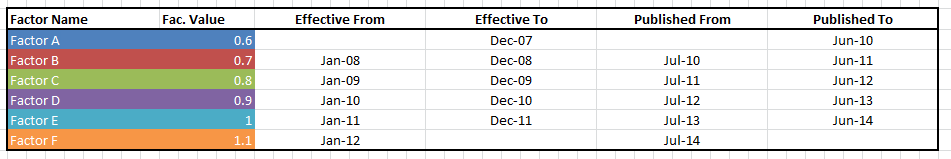
First period: Using only effective dates. Beginning anytime in the past and going up to "Effective To"
Second period: Beginning immediately after the date of "Effective To" for the factor where "Published From" occurred before historical load date and ending the month before the next factor is published ("Published From"). This period represents the time lag between when the last set of factors were effective and the new set have been published.
Third period: Beginning with "Published From"
Example scenario: Historical Load Date = March 2012
In this scenario, an organization joined Envizi in October 2012 and instructed Envizi to load historical data up to March 2012 using the most up-to-date factors available at that time. At this point in time (October 2012), the only factors published were Factors A, B, C and D since these factors are typically published in July (see Published From column in table above).
Therefore all historical data loaded up to March 2012 will use only factors that were available at that time. This includes Factors A, B and C and covers the time period up until Dec 2009.
After December 2009, Factor C will continue to be used. In July 2012, a new factor is published for the 2010 calendar year, but since the organization has already published emissions figures for 2010 and earlier, and does not want their data recalculated, Envizi only applies this factor going forward from July 2012 onwards.
Therefore, the period between January 2010 and June 2012 (represented by the thick outlined box) uses the most up-to-date factor that was available during that period, which in this case was Factor C.
Activity data entered at any point during or after July 2012 will use the most up-to-date factor available. This is accomplished by applying factors using the published dates rather than effective dates for all data after the Historical Load Date.
Factor Effective and Published Dates for Residual Mix Factor Sets
Factor Set | Factor Source | Effective From | Effective To | Published From | Published To | Review Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
USA - Market-based electricity Green-e | 2015 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 31/12/2013 | 31/03/2016 | ||||
2016 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 1/01/2014 | 31/12/2014 | 1/04/2016 | 31/03/2017 | |||
2017 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 1/01/2015 | 31/12/2015 | 1/04/2017 | 31/03/2018 | |||
2018 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 1/01/2016 | 31/12/2016 | 1/04/2018 | 31/05/2019 | |||
2019 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 1/01/2017 | 31/12/2017 | 1/06/2019 | 30/04/2020 | |||
2020 Green-e Energy Residual Mix Emissions Rates. | 1/01/2018 | 1/05/2020 | 1-Jun-21 | Historical effective dates updated on 21/Sep/2020 to reflect the data used to compile emission factors. | |||
Europe - Market-based electricity AIB | 2012 RE-DISS - Phase II. | 31/12/2012 | 31/12/2012 | ||||
2013 RE-DISS - Phase II. | 1/01/2013 | 31/12/2013 | 1/01/2013 | 31/12/2013 | |||
2014 RE-DISS - Phase II. | 1/01/2014 | 31/12/2014 | 1/01/2014 | 31/12/2014 | |||
2015 AIB. European Residual Mixes | 1/01/2015 | 31/12/2015 | 1/01/2015 | 31/12/2015 | |||
2016 AIB. European Residual Mixes | 1/01/2016 | 31/12/2016 | 1/01/2016 | 31/12/2016 | |||
2017 AIB. European Residual Mixes | 1/01/2017 | 31/12/2017 | 1/01/2017 | 31/12/2017 | |||
2018 AIB. European Residual Mixes | 1/01/2018 | 31/12/2018 | 1/01/2018 | 30/04/2020 | Published dates are used from this publication onwards. | ||
2019 AIB. European Residual Mixes | 1/01/2019 | 1/05/2020 | 1-Jun-21 |
Options
Also note that if your organization would prefer to only use effective dates, this is possible too (by setting the historical data load to blank – i.e, clearing the date). If this is the case then the organization's emissions will change over time as Envizi loads new factors. On the other hand, if your organization would prefer to only use published dates, this can be accomplished by setting the Historical Load Date to be less than the first start date of the organization's first activity data.
